彩票中的所有组合被抽奖的可能性均等,因为只有一种方法可以赢得大奖。

那么这是否意味着5-10-15-20-25-30也有可能?
没有。
您会看到,如果继续从一个侧面看彩票,则可能会妨碍自己查看整个图片。
您必须了解组合是由数字组成的。
组成很重要。
在彩票中,组合被组合成组合组。并且组合组具有不同的概率。
如果您选择从错误的组中选择组合,那么您获胜的可能性将受到极大影响。
而且您可能会继续以极低的概率演奏组合。
有什么证据?
好吧,我想最好的证据是向您展示一些计算,然后使用实际的抽奖来证明我的计算。
使用概率论,我们可以计算组合在平局中将如何发生。我们可以衡量最佳组合和最差组合之间的差异。
不幸的是,概率计算因彩票而异。没有一种万能的计算方法。
因此,出于说明目的,我将使用乐透6/49系统作为基础。不用担心 您将在计算器部分的最喜欢的彩票系统中查看计算结果。
以下是乐透6/49系统中组合的样本类型。
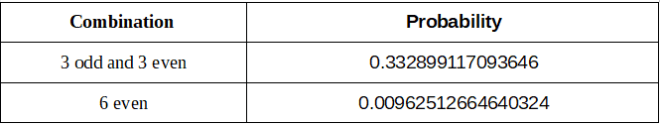
由所有偶数组成的组合只能在100次抽奖中出现一次,而平衡的奇偶组合在100次抽奖中可以出现33次。
如果我们想知道这两组在1000次抽奖中将如何发生,我们只需要将抽奖次数乘以它们相应的概率即可。
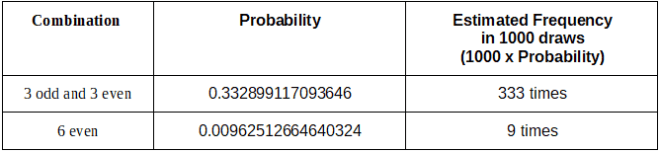
数字不会说谎。
这种概率的预测能力将帮助您将无知的玩家变成有见识的乐透玩家。
简而言之,错误的组合会导致金钱浪费。
正确的组合选择可以使您的彩票有个不错的选择。
感谢组合数学和概率论,因为我们有办法知道您是否走上了正确的道路。
例如,诸如1-2-3-4-5-6的组合将对5-17-21-37-39-43和4-10-18-22-36-48表现出不同的概率。
当然,以上数字只是乐透6/49游戏中许多组合中的三个,而这些组合中最难被吸引。
让我们讨论为什么。
为什么组合不显示均等概率?
让我解释一下在罐子中使用两种简单类型的大理石的方法。黄色和红色大理石代表彩票中组合的类型。
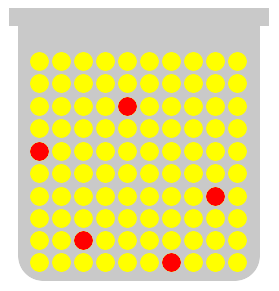
如您所见,黄色大理石比五个红色大理石要多。概率说明,当您闭上眼睛从罐子中随机挑选大理石时,您很可能会得到黄色。
您的第二个和第三个选择将更可能是黄色大理石,因为与红色大理石相比,黄色大理石更容易被拾取。
在数学中,我们通过以下方式表示两种类型的大理石的概率:
P(黄色)= 95/100或95%
P(红色)= 5/100或05%
在十进制表示中,我们通过以下方式表示概率度量:
P(黄色)= 95/100或0.95
P(红色)= 5/100或0.05
假设我们在每次试验中重置了大理石的数量,则每100次抽奖中黄色大理石将被选出95次。那么每100次抽奖中只有红色大理石会被选择5次。
预期频率(黄色球)= 100 x 0.95 = 95倍
预期频率(红球)= 100 x 0.05 = 5倍
在随机游戏(例如彩票)中,相同的概率原理也具有规则性。
让我给您一些确凿的证据,证明彩票中的组合确实显示出不同的概率。
奇/偶组合
让我们将49个数字分为两组。
奇数= {1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19,21,23,25,27,29,31,33,35,37,39,41,43,45,47 ,49}
偶数= {2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20,22,24,26,28,30,32,34,36,38,40,42,44,46,48 }
我们有25个奇数和24个偶数。
两组代表乐透6/49游戏的49个球。
从这两组中,我们可以产生以下类型的组合:
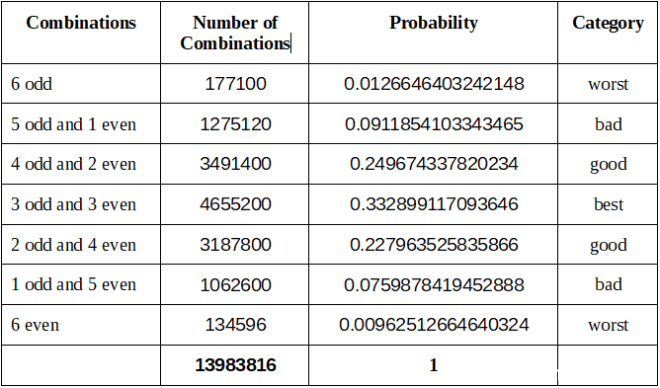
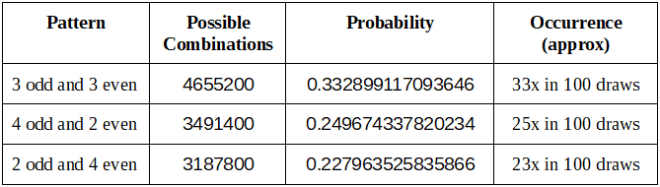
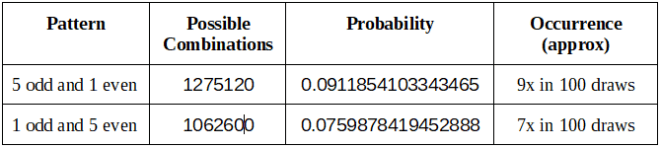
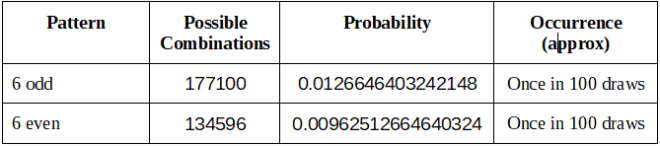
每个奇/偶模式都包含一定数量的可能组合。他们的总数代表乐透6/49游戏的所有可能组合,即13,983,816。并且它们的所有概率之和应等于1。
从上表中可以看出,在乐透6/49游戏中被抽奖的机率最高的是三奇三偶模式。预计这组组合会在100次抽奖中出现33次。
因此,由所有偶数或所有奇数组成的那些组合是最差的组合。
值得注意的是,某些组合既未分类为最佳,也未分类为最差。这些组合被认为是中间的。这些组合的使用取决于您的判断。
下表应指导所有乐透6/49玩家在乐透6/49开奖中玩什么组合。
推荐组合
中型组合
(取决于您使用这些组合)
避免组合
实际彩票结果与理论计算
我已经证明,从理论的角度来看,组合没有被抽中的机会相等。
现在,让我们通过将计算结果与实际彩票结果进行比较来证明这一点。
正如我所说,我们使用概率来衡量在给定抽奖次数中组合出现的可能性。因此,通过将概率值乘以一定数量的平局,我们可以得出给定数量的平局中组合的预期频率。
预期频率=概率x抽奖次数
为了证明我们的理论计算是正确的,预期频率应与实际频率紧密匹配。
从2006年1月7日到2018年9月29日,澳大利亚星期六乐透 664开奖
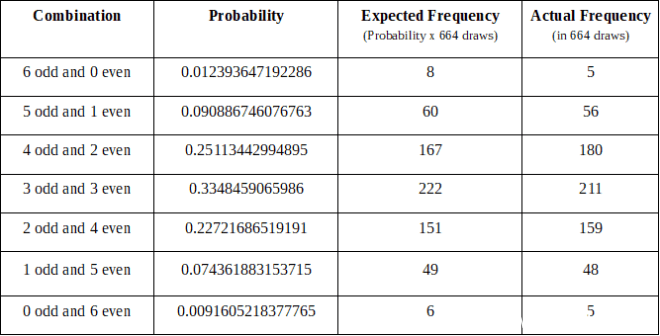
您能注意到预期频率与实际频率之间的紧密匹配吗?
请注意,概率仅是一种指导。不要期望值将始终匹配。有时候他们会。
当然,这种概率分析不仅适用于澳大利亚彩票。概率论适用于所有彩票系统。
如您所见,上表证明组合组的概率不相等。
让我们继续其他彩票系统,以进一步证明我们的观点。
美国强力球
309从2015年10月7日到2018年9月29日抽奖
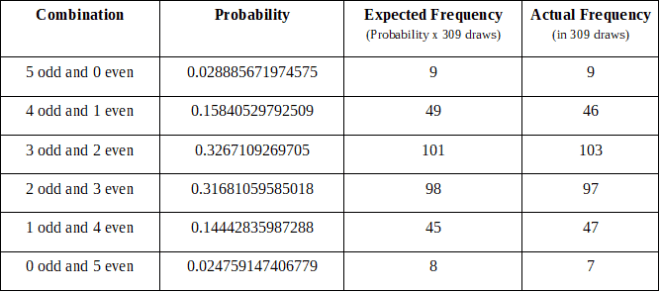
注意:我们对美国强力球的分析必须从 2015 年10月7日开始,因为这是彩票官员开始实施5/69格式的日期。
如果您注意到这一点,则理论概率和实际彩票结果都同意组合组具有不同的概率。我们可以一次又一次地证明这一点。
下表应说明一切。
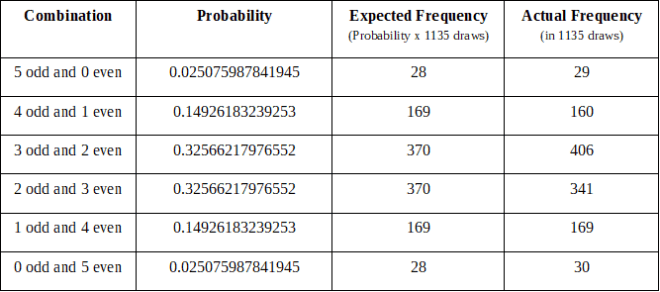
从2004年4月16日到2018年9月28日共抽奖1,135 欧元
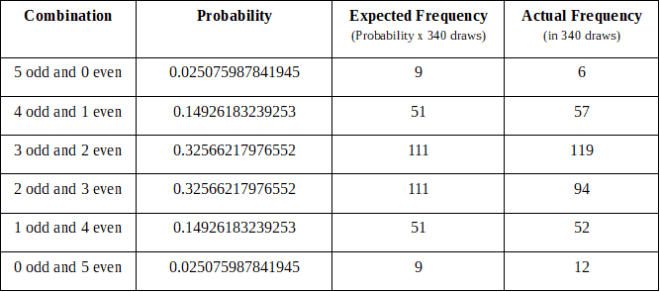
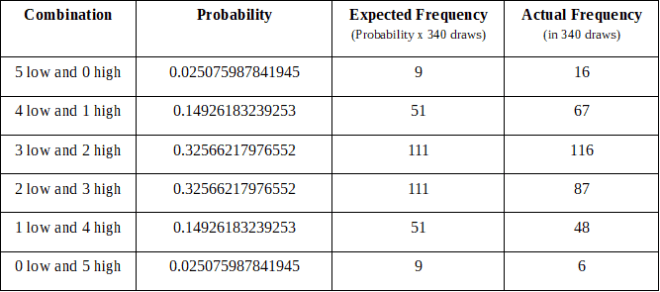
从2012年3月23日至2018年9月28日,欧洲头奖 340开奖
爱尔兰乐透
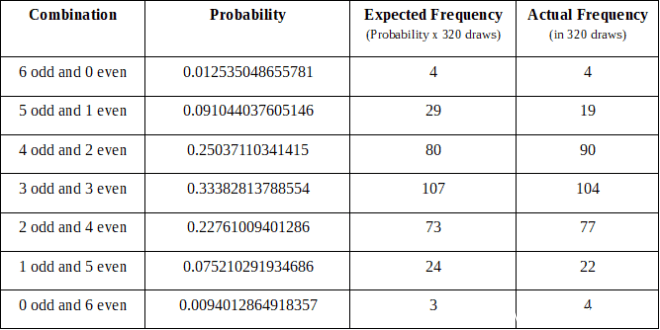
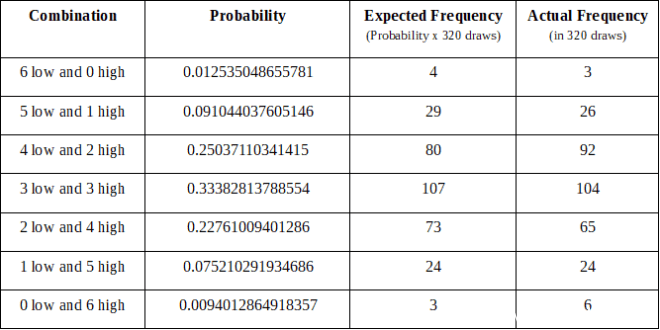
320抽奖时间为2015年9月5日至2018年9月29日
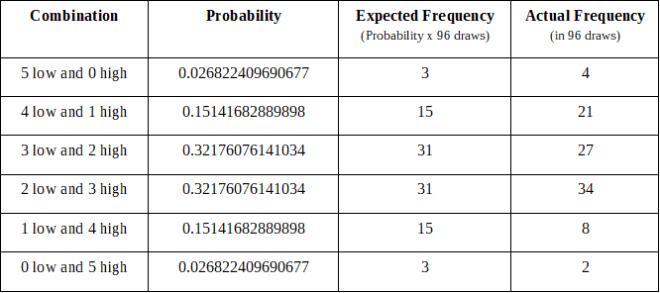
从2017年10月31日到2018年9月28日,美国超级百万富翁共抽奖96次
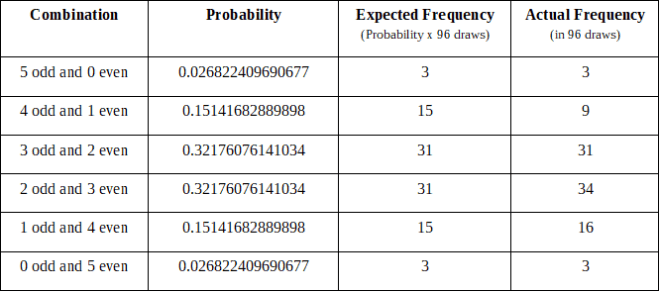
注意:我们对美国百万富翁的分析必须从 2017 年10月31日开始,因为这是彩票官员开始实施5/70格式的日期。
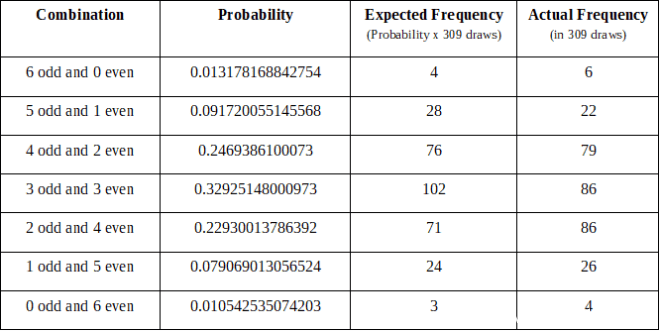
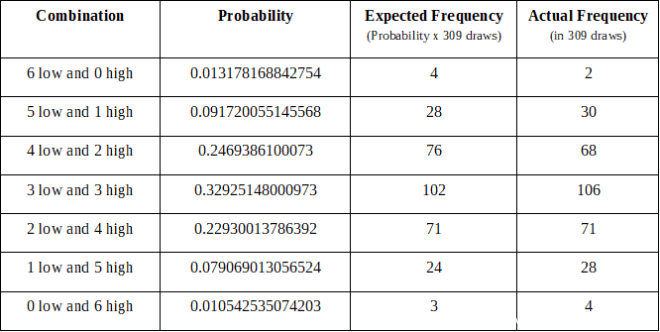
从2015年10月10日至2018年9月29日抽奖英国彩票 309
低/高组合
除了奇数和偶数之外,数字还可以分为高和低。让我们将49个数字分为两组:
低= {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24 ,25}
高= {26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49 }
在这两个集合中,我们的概率分析表明,获胜数字倾向于在整个数字字段中平均分配,因为大多数获胜组合由较低集合的3个数字和较高集合的三个数字组成。
同样,鼓励玩家远离由纯数字或纯数字组成的组合。
下表显示了我们可以从两组低数和高数产生的所有组合类型。
推荐组合
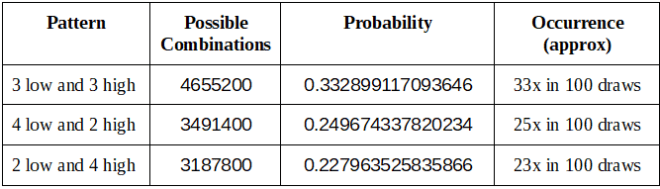
中型组合
(取决于您使用这些组合)
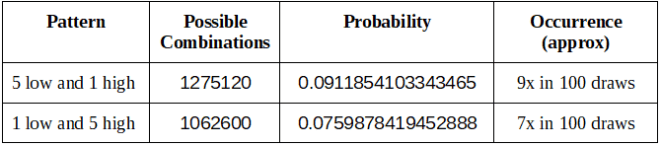
避免的模式
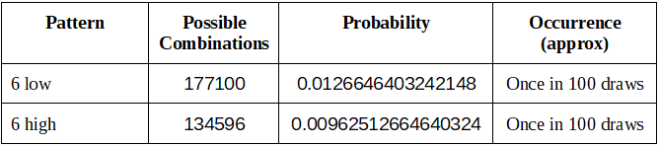
实际彩票结果与理论计算
同样,理论计算和实际彩票结果都同意,某些组合的效果要好于其他组合。
请看下表:
从2006年1月7日到2018年9月29日,澳大利亚星期六乐透 664开奖
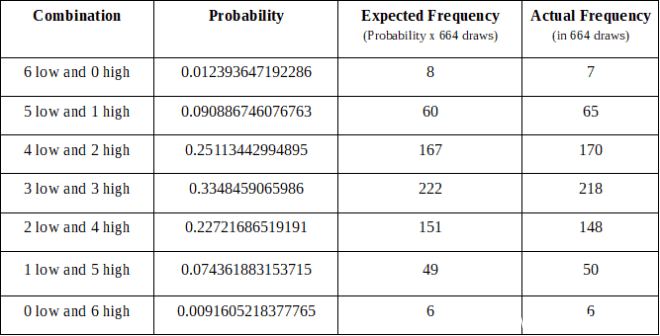
美国强力球
309从2015年10月7日到2018年9月29日抽奖
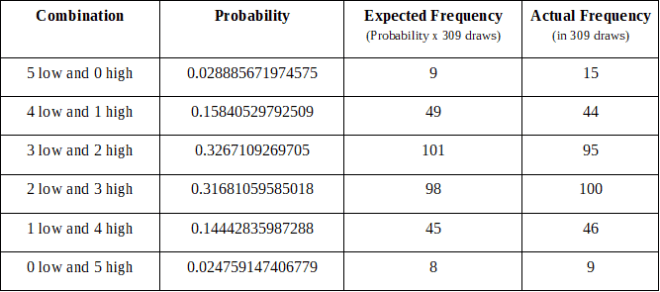
注意:我们对美国强力球的分析必须从2015年10月7日开始,因为这是彩票官员开始实施5/69格式的日期。
从2004年4月16日到2018年9月28日共抽奖1,135 欧元
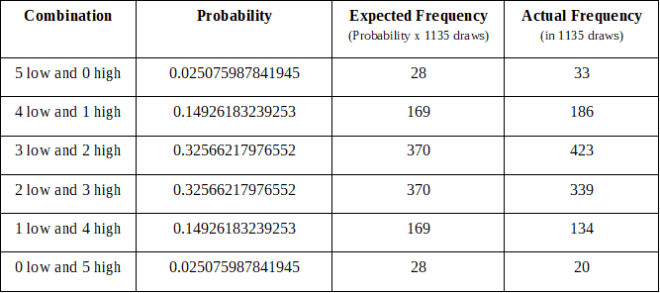
从2012年3月23日至2018年9月28日,欧洲头奖 340开奖
爱尔兰乐透
320抽奖时间为2015年9月5日至2018年9月29日
从2017年10月31日到2018年9月28日,美国百万富翁 96开奖
注意:我们对美国百万富翁的分析必须从2017年10月31日开始,因为这是彩票官员开始实施5/70格式的日期。
从2015年10月10日至2018年9月29日抽奖英国彩票 309
下一步是什么?
概率分析可能会出现问题并且非常混乱。
例如,诸如1-2-3-4-5-6的组合由3奇数3偶数组成。根据我们的奇/偶分析,这种组合被认为是最好的组合之一。
但是我们知道这是不正确的,因为从我们的低/高分析来看,一个纯粹由小数组成的组合具有较低的概率。
All combinations in the lottery have an equal probability of getting drawn because there’s only one way to win the jackpot.

So does that mean 5-10-15-20-25-30 is equally likely?
No.
You see, if you keep on looking at the lottery from a one-sided perspective, you are sort of preventing yourself from seeing the whole picture.
You have to understand that combination has a composition of numbers.
And composition matters.
In the lottery, combinations are put together in combinatorial groups. And combinatorial groups have a different probability.
If you choose to pick your combination from a wrong group, then your probability of winning will be drastically affected.
And you probably keep playing combinations with very low probability.
What’s the evidence?
Well, I guess the best evidence is to show you a couple of calculations then use the actual lottery draws to prove my calculation.
With the use of probability theory, we can calculate how a combination will likely occur in a draw. We can measure the difference between the best combinations and the worst ones.
Unfortunately, probability calculation differs from one lottery to another. There’s no one-size-fits-all calculation.
So for illustration, I will use the lotto 6/49 system as the basis. Don’t worry. You will get to see the calculation in your favorite lottery system in the calculator section.
Below is a sample type of combinations in a lotto 6/49 system.

A combination that consists of all even numbers can only occur once in 100 draws while a balanced odd and even combination can occur 33 times in 100 draws.
If we want to know how these two groups will occur in 1000 draws, we only need to multiply the number of draws by their corresponding probability.

Numbers don’t lie.
This predictive power of probability will help turn you into a clueless gamer into an informed lotto player.
Simply put, wrong combinations lead to a waste of money.
The right choice of combination leads to a good shot at the lottery.
Thanks to combinatorial math and probability theory because we have the means to know whether or not you’re on the right track.
For example, a combination such as 1-2-3-4-5-6 will exhibit different probability against 5-17-21-37-39-43 and 4-10-18-22-36-48.
Of course, the above numbers are just three of the many combinations in lotto 6/49 games that possess the poorest chance of getting drawn.
Let’s discuss why.
Why Don’t Combinations Exhibit Equal Probability?
Let me explain with the use of two simple types of marbles in a jar. The yellow and the red color marbles represent the types of combinations in the lottery.

As you see, the yellow marbles outnumbered the five red marbles. Probability explains that when you randomly pick a marble from a jar with your eyes closed, you will more likely get a yellow one.
Your second and third pick will be more likely yellow marbles again because the probability leans towards the yellow marbles getting picked more often than the red ones.
In mathematics, we express the probability of the two types of marbles in the following ways:
P(yellow) = 95/100 or 95%
P(red) = 5/100 or 05%
In decimal presentations, we express the probability measurement in the following way:
P(yellow) = 95/100 or 0.95
P(red) = 5/100 or 0.05
Assuming we reset the number of marbles in each trial, the yellow marbles will get picked 95 times in every 100 draws. Then the red marbles will only get picked 5 times in every 100 draws.
Expected Frequency (yellow ball) = 100 x 0.95 = 95 times
Expected Frequency (red ball) = 100 x 0.05 = 5 times
The same probability principle rules in a random game such as the lottery.
Let me give you some solid evidence that, indeed, combinations in the lottery exhibit different probabilities.
Odd/Even Combinations
Let’s group 49 numbers in two sets.
Odd = {1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19,21,23,25,27,29,31,33,35,37,39,41,43,45,47,49}
Even = {2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20,22,24,26,28,30, 32,34,36,38,40,42,44,46,48}
We have 25 odd numbers and 24 even numbers.
The two sets represent the 49 balls of a Lotto 6/49 game.
Out of these 2 sets, we can produce the following types of combinations:

Each odd/even pattern holds a certain number of possible combinations. Their total represents all the possible combinations in a lotto 6/49 game, which is 13,983,816. And the sum of all their probabilities should equal to 1.
From the table above, we see that it’s the 3-odd-3-even pattern that exhibits the best probability of getting drawn in a lotto 6/49 game. This group of combination is expected to occur 33 times in 100 draws.
And accordingly, those combinations which consist of either all even or all odd numbers are the worst combinations.
Noticeably, some combinations are neither categorized as best nor worst. These combinations are considered the middle ones. The use of these groups of combinations is up to your judgment.
The following tables below should guide all lotto 6/49 players what combinations to play in a lotto 6/49 draw.
Recommended Combinations

Middle Type Combinations
(Playing with these combinations is up to you)

Combinations to Avoid

Actual Lottery Results Versus Theoretical Calculation
I have shown that combinations don’t have an equal chance of getting drawn from a theoretical point of view.
Now, let’s prove it by comparing our calculation with the actual lottery results.
As I said, we use probability to measure how likely a combination will occur in a given number of draws. So by multiplying probability value by a certain number of draws, we get the expected frequency of the combination in that given number of draws.
Expected frequency = Probability x number of draws
And to prove that our theoretical calculation is correct, the expected frequency should closely match the actual frequency.
Australian Saturday Lotto
664 draws from January 7, 2006, to September 29, 2018

Can you notice the close match between expected frequency and actual frequency?
Take note that probability is simply a guide. Don’t expect that values will always match. Sometimes they do.
Of course, this probability analysis does not only apply to the Australian lottery. Probability theory applies to all lottery systems.
And as you see, the above table proves that combinatorial groups don’t have equal probability.
Let’s move on to other lottery systems to prove our point further.
U.S Powerball
309 draws from October 7, 2015 to September 29, 2018

Note: Our analysis of the U.S. Powerball must start on October 7, 2015 because this was the date when lottery officials began to implement the 5/69 format.
If you are noticing it, both theoretical probability and the actual lottery results agree that combinatorial groups have different probabilities. And we can prove it again and again.
The following tables below should speak for themselves.
Euro Millions
1,135 draws from April 16, 2004 to September 28, 2018

Euro Jackpot
340 draws from March 23, 2012 to September 28, 2018

Irish Lotto
320 draws from September 5, 2015 to September 29, 2018

U.S. Mega Millions
96 total draws From October 31, 2017 to September 28, 2018

Note: Our analysis of the U.S. Mega Millions must start on October 31, 2017 because this was the date when lottery officials began to implement the 5/70 format.
UK Lottery
309 draws from October 10, 2015 to September 29, 2018

Low/High Combinations
Aside from odd and even, numbers can be grouped into low and high. Let’s group 49 numbers in two sets:
Low = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25}
High = {26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49}
Out of these two sets, our probability analysis shows that winning numbers tend to be evenly distributed in the entire number field as the majority of the winning combinations consist of 3 numbers from the lower set and three numbers from the higher set.
Similarly, players are encouraged to stay away from a combination that consists of purely low numbers or purely high numbers.
Below are the tables showing all the types of combinations we can produce from the two sets of low and high numbers.
Recommended Combinations

Middle Type Combinations
(Playing with these combinations is up to you)

Patterns to Avoid

Actual Lottery Results Versus Theoretical Calculation
Again, both theoretical calculation and the actual lottery results agree that some combinations perform better than others.
Take a look at the following tables below:
Australian Saturday Lotto
664 draws from January 7, 2006 to September 29, 2018

U.S Powerball
309 draws from October 7, 2015 to September 29, 2018

Note: Our analysis of the U.S. Powerball must start on October 7, 2015, because this was the date when lottery officials began to implement the 5/69 format.
Euro Millions
1,135 draws from April 16, 2004 to September 28, 2018

Euro Jackpot
340 draws from March 23, 2012 to September 28, 2018

Irish Lotto
320 draws from September 5, 2015 to September 29, 2018

U.S. Mega Millions
96 draws from October 31, 2017 to September 28, 2018

Note: Our analysis of the U.S. Mega Millions must start on October 31, 2017, because this was the date when lottery officials began to implement the 5/70 format.
UK Lottery
309 draws from October 10, 2015 to September 29, 2018

What’s Next?
Probability analysis can be problematic and quite confusing.
For example, a combination such as 1-2-3-4-5-6 consists of 3-odd-3-even numbers. According to our odd/even analysis, such combination is considered one of the best ones.
But we know it’s not true because conversely from our low/high analysis, a combination that is made of purely small numbers possesses an inferior probability.
Alle Kombinationen in der Lotterie haben die gleiche Wahrscheinlichkeit, gezogen zu werden, da es nur einen Weg gibt, den Jackpot zu gewinnen.

Bedeutet das also, dass 5-10-15-20-25-30 gleich wahrscheinlich ist?
Nein.
Sie sehen, wenn Sie die Lotterie weiterhin aus einer einseitigen Perspektive betrachten, verhindern Sie, dass Sie das ganze Bild sehen.
Sie müssen verstehen, dass die Kombination aus Zahlen besteht.
Und Komposition ist wichtig.
In der Lotterie werden Kombinationen in kombinatorischen Gruppen zusammengefasst. Und kombinatorische Gruppen haben eine andere Wahrscheinlichkeit.
Wenn Sie Ihre Kombination aus einer falschen Gruppe auswählen, wird Ihre Gewinnwahrscheinlichkeit drastisch beeinflusst.
Und Sie spielen wahrscheinlich weiterhin Kombinationen mit sehr geringer Wahrscheinlichkeit.
Was ist der Beweis?
Nun, ich denke, der beste Beweis ist, Ihnen ein paar Berechnungen zu zeigen und dann die tatsächlichen Lotterieverlosungen zu verwenden, um meine Berechnung zu beweisen.
Mit Hilfe der Wahrscheinlichkeitstheorie können wir berechnen, wie wahrscheinlich eine Kombination bei einem Unentschieden sein wird. Wir können den Unterschied zwischen den besten und den schlechtesten Kombinationen messen.
Leider unterscheidet sich die Wahrscheinlichkeitsberechnung von Lotterie zu Lotterie. Es gibt keine Einheitsberechnung.
Zur Veranschaulichung werde ich das Lotto 6/49 System als Grundlage verwenden. Mach dir keine Sorgen. Sie können die Berechnung in Ihrem bevorzugten Lotteriesystem im Abschnitt “Rechner” sehen.
Unten finden Sie ein Beispiel für eine Kombination in einem Lotto 6/49-System.

Eine Kombination, die aus allen geraden Zahlen besteht, kann nur einmal in 100 Zügen auftreten, während eine ausgeglichene ungerade und gerade Kombination in 100 Zügen 33 Mal vorkommen kann.
Wenn wir wissen wollen, wie diese beiden Gruppen in 1000 Ziehungen auftreten, müssen wir nur die Anzahl der Ziehungen mit ihrer entsprechenden Wahrscheinlichkeit multiplizieren.

Zahlen lügen nicht.
Diese Vorhersagekraft der Wahrscheinlichkeit wird Ihnen helfen, aus einem ahnungslosen Spieler einen informierten Lottospieler zu machen.
Einfach ausgedrückt führen falsche Kombinationen zu Geldverschwendung.
Die richtige Wahl der Kombination führt zu einem guten Schuss bei der Lotterie.
Dank kombinatorischer Mathematik und Wahrscheinlichkeitstheorie können wir wissen, ob Sie auf dem richtigen Weg sind oder nicht.
Beispielsweise zeigt eine Kombination wie 1-2-3-4-5-6 eine unterschiedliche Wahrscheinlichkeit gegenüber 5-17-21-37-39-43 und 4-10-18-22-36-48.
Natürlich sind die oben genannten Zahlen nur drei der vielen Kombinationen in Lotto 6/49 Spielen, die die geringste Chance haben, unentschieden zu werden.
Lassen Sie uns diskutieren, warum.
Warum weisen Kombinationen nicht die gleiche Wahrscheinlichkeit auf?
Lassen Sie mich anhand von zwei einfachen Arten von Murmeln in einem Glas erklären. Die gelben und roten Murmeln repräsentieren die Arten von Kombinationen in der Lotterie.

Wie Sie sehen, waren die gelben Murmeln den fünf roten Murmeln überlegen. Die Wahrscheinlichkeit erklärt, dass Sie eher einen gelben erhalten, wenn Sie zufällig einen Marmor mit geschlossenen Augen aus einem Glas nehmen.
Bei Ihrer zweiten und dritten Auswahl handelt es sich wahrscheinlich wieder um gelbe Murmeln, da sich die Wahrscheinlichkeit eher zu gelben Murmeln neigt als zu roten.
In der Mathematik drücken wir die Wahrscheinlichkeit der beiden Arten von Murmeln folgendermaßen aus:
P (gelb) = 95/100 oder 95%
P (rot) = 5/100 oder 05%
In Dezimaldarstellungen drücken wir die Wahrscheinlichkeitsmessung folgendermaßen aus:
P (gelb) = 95/100 oder 0,95
P (rot) = 5/100 oder 0,05
Angenommen, wir setzen die Anzahl der Murmeln in jedem Versuch zurück, werden die gelben Murmeln 95 Mal pro 100 Ziehungen ausgewählt. Dann werden die roten Murmeln nur fünfmal pro 100 Ziehungen gepflückt.
Erwartete Frequenz (gelber Ball) = 100 x 0,95 = 95 mal
Erwartete Frequenz (rote Kugel) = 100 x 0,05 = 5 mal
Das gleiche Wahrscheinlichkeitsprinzip gilt für ein zufälliges Spiel wie die Lotterie.
Lassen Sie mich einige solide Beweise dafür geben, dass Kombinationen in der Lotterie tatsächlich unterschiedliche Wahrscheinlichkeiten aufweisen.
Ungerade / gerade Kombinationen
Lassen Sie uns 49 Zahlen in zwei Sätzen gruppieren.
Ungerade = {1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19,21,23,25,27,29,31,33,35,37,39,41,43,45,47 , 49}
Gerade = {2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20,22,24,26,28,30, 32,34,36,38,40,42,44,46,48 }}
Wir haben 25 ungerade und 24 gerade Zahlen.
Die beiden Sätze repräsentieren die 49 Bälle eines Lotto 6/49 Spiels.
Aus diesen beiden Sätzen können wir die folgenden Arten von Kombinationen herstellen:

Jedes ungerade / gerade Muster enthält eine bestimmte Anzahl möglicher Kombinationen. Ihre Summe repräsentiert alle möglichen Kombinationen in einem Lotto 6/49 Spiel, das 13.983.816 ist. Und die Summe aller ihrer Wahrscheinlichkeiten sollte gleich 1 sein.
Aus der obigen Tabelle geht hervor, dass es das 3-ungerade-3-gerade-Muster ist, das die beste Wahrscheinlichkeit aufweist, in einem Lotto-6/49-Spiel gezogen zu werden. Diese Gruppe von Kombinationen wird voraussichtlich 33 Mal in 100 Ziehungen auftreten.
Und dementsprechend sind diejenigen Kombinationen, die entweder aus allen geraden oder allen ungeraden Zahlen bestehen, die schlechtesten Kombinationen.
Bemerkenswerterweise werden einige Kombinationen weder als beste noch als schlechteste eingestuft. Diese Kombinationen gelten als die mittleren. Die Verwendung dieser Kombinationsgruppen liegt in Ihrem Ermessen.
Die folgenden Tabellen sollen allen Lotto 6/49 Spielern zeigen, welche Kombinationen sie bei einem Lotto 6/49 Unentschieden spielen sollen.
Empfohlene Kombinationen

Kombinationen vom mittleren Typ
(Das Spielen mit diesen Kombinationen liegt bei Ihnen)

Zu vermeidende Kombinationen

Tatsächliche Lotterieergebnisse versus theoretische Berechnung
Ich habe gezeigt, dass Kombinationen aus theoretischer Sicht nicht die gleiche Chance haben, gezeichnet zu werden.
Lassen Sie es uns nun beweisen, indem wir unsere Berechnung mit den tatsächlichen Lotterieergebnissen vergleichen.
Wie gesagt, wir verwenden die Wahrscheinlichkeit, um zu messen, wie wahrscheinlich eine Kombination bei einer bestimmten Anzahl von Ziehungen auftritt. Durch Multiplizieren des Wahrscheinlichkeitswerts mit einer bestimmten Anzahl von Ziehungen erhalten wir die erwartete Häufigkeit der Kombination in dieser gegebenen Anzahl von Ziehungen.
Erwartete Häufigkeit = Wahrscheinlichkeit x Anzahl der Ziehungen
Und um zu beweisen, dass unsere theoretische Berechnung korrekt ist, sollte die erwartete Frequenz eng mit der tatsächlichen Frequenz übereinstimmen.
Das australische Samstagslotto
664 wird vom 7. Januar 2006 bis zum 29. September 2018 gezogen

Können Sie die enge Übereinstimmung zwischen erwarteter Frequenz und tatsächlicher Frequenz feststellen?
Beachten Sie, dass die Wahrscheinlichkeit nur ein Anhaltspunkt ist. Erwarten Sie nicht, dass die Werte immer übereinstimmen. Manchmal tun sie es.
Natürlich gilt diese Wahrscheinlichkeitsanalyse nicht nur für die australische Lotterie. Die Wahrscheinlichkeitstheorie gilt für alle Lotteriesysteme.
Und wie Sie sehen, zeigt die obige Tabelle, dass kombinatorische Gruppen nicht die gleiche Wahrscheinlichkeit haben.
Gehen wir zu anderen Lotteriesystemen über, um unseren Standpunkt weiter zu beweisen.
Der US Powerball
309 zieht vom 7. Oktober 2015 bis zum 29. September 2018

Hinweis: Unsere Analyse des US Powerball muss am 7. Oktober 2015 beginnen, da an diesem Tag die Lotteriebeamten mit der Implementierung des 5/69-Formats begannen.
Wenn Sie es bemerken, stimmen sowohl die theoretische Wahrscheinlichkeit als auch die tatsächlichen Lotterieergebnisse darin überein, dass kombinatorische Gruppen unterschiedliche Wahrscheinlichkeiten haben. Und wir können es immer wieder beweisen.
Die folgenden Tabellen sollten für sich selbst sprechen.
Euro Millions
1.135 zieht vom 16. April 2004 bis 28. September 2018

Der Euro Jackpot
340 wird vom 23. März 2012 bis zum 28. September 2018 gezogen

Das Irish Lotto
320 zieht vom 5. September 2015 bis zum 29. September 2018

US Mega Millions
96 insgesamt Ziehungen Vom 31. Oktober 2017 bis 28. September 2018

Hinweis: Unsere Analyse der US Mega Millions muss am 31. Oktober 2017 beginnen, da an diesem Tag die Lotteriebeamten mit der Implementierung des 5/70-Formats begannen.
Die UK Lottery
309 zieht vom 10. Oktober 2015 bis zum 29. September 2018

Niedrige / hohe Kombinationen
Abgesehen von ungeraden und geraden können Zahlen in niedrig und hoch gruppiert werden. Gruppieren wir 49 Zahlen in zwei Sätzen:
Niedrig = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24 , 25}
Hoch = {26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49 }}
Aus diesen beiden Sätzen zeigt unsere Wahrscheinlichkeitsanalyse, dass die Gewinnzahlen tendenziell gleichmäßig im gesamten Zahlenfeld verteilt sind, da die Mehrheit der Gewinnkombinationen aus 3 Zahlen aus dem unteren Satz und drei Zahlen aus dem höheren Satz besteht.
Ebenso wird den Spielern empfohlen, sich von einer Kombination fernzuhalten, die aus rein niedrigen oder rein hohen Zahlen besteht.
In der folgenden Tabelle sind alle Arten von Kombinationen aufgeführt, die wir aus den beiden Sätzen niedriger und hoher Zahlen erstellen können.
Empfohlene Kombinationen

Kombinationen vom mittleren Typ
(Das Spielen mit diesen Kombinationen liegt bei Ihnen)

Zu vermeidende Muster

Tatsächliche Lotterieergebnisse versus theoretische Berechnung
Auch hier stimmen sowohl die theoretische Berechnung als auch die tatsächlichen Lotterieergebnisse darin überein, dass einige Kombinationen besser abschneiden als andere.
Schauen Sie sich die folgenden Tabellen an:
Das australische Samstagslotto
664 wird vom 7. Januar 2006 bis zum 29. September 2018 gezogen

Der US Powerball
309 zieht vom 7. Oktober 2015 bis zum 29. September 2018

Hinweis: Unsere Analyse des US Powerball muss am 7. Oktober 2015 beginnen, da an diesem Tag die Lotteriebeamten mit der Implementierung des 5/69-Formats begannen.
Euro Millions
1.135 zieht vom 16. April 2004 bis 28. September 2018

Der Euro Jackpot
340 wird vom 23. März 2012 bis zum 28. September 2018 gezogen

Das Irish Lotto
320 zieht vom 5. September 2015 bis zum 29. September 2018

US Mega Millions
96 zieht vom 31. Oktober 2017 bis zum 28. September 2018

Hinweis: Unsere Analyse der US Mega Millions muss am 31. Oktober 2017 beginnen, da an diesem Tag die Lotteriebeamten mit der Implementierung des 5/70-Formats begannen.
Die UK Lottery
309 zieht vom 10. Oktober 2015 bis zum 29. September 2018

Was kommt als nächstes?
Die Wahrscheinlichkeitsanalyse kann problematisch und ziemlich verwirrend sein.
Zum Beispiel besteht eine Kombination wie 1-2-3-4-5-6 aus 3-ungeraden-3-geraden Zahlen. Nach unserer ungeraden / geraden Analyse wird eine solche Kombination als eine der besten angesehen.
Wir wissen jedoch, dass dies nicht der Fall ist, da umgekehrt aus unserer Low / High-Analyse eine Kombination aus rein kleinen Zahlen eine geringere Wahrscheinlichkeit besitzt.
Все комбинации в лотерее имеют одинаковую вероятность выиграть, потому что есть только один способ выиграть джекпот.

Значит ли это, что 5-10-15-20-25-30 одинаково вероятны?
Нет.
Видите ли, если вы продолжаете смотреть на лотерею с односторонней точки зрения, вы как бы мешаете себе увидеть всю картину.
Вы должны понимать, что комбинация имеет композицию чисел.
И состав имеет значение.
В лотерее комбинации объединяются в комбинаторные группы. И комбинаторные группы имеют разную вероятность.
Если вы решите выбрать свою комбинацию из неправильной группы, то вероятность вашего выигрыша будет существенно снижена
И вы, вероятно, продолжаете играть комбинации с очень низкой вероятностью.
Какие доказательства?
Ну, я думаю, лучшее доказательство – показать вам пару расчетов, а затем использовать фактические лотереи, чтобы доказать мои расчеты.
Используя теорию вероятностей, мы можем рассчитать, как комбинация, вероятно, произойдет при ничьей. Мы можем измерить разницу между лучшими комбинациями и худшими.
К сожалению, расчет вероятности отличается от одной лотереи к другой. Там нет единого расчета для всех.
Поэтому для иллюстрации я буду использовать систему лото 6/49 в качестве основы. Не беспокойся Вы можете увидеть расчет в вашей любимой лотерее в разделе калькулятора.
Ниже приведен пример типа комбинаций в системе лото 6/49.

Комбинация, состоящая из всех четных чисел, может встречаться только один раз в 100 тиражах, в то время как сбалансированная нечетная и четная комбинация может встречаться 33 раза в 100 тиражах.
Если мы хотим знать, как эти две группы будут происходить в 1000 тиражах, нам нужно только умножить количество тиражей на их соответствующую вероятность.

Числа не лгут.
Эта предсказательная сила вероятности поможет превратить вас в бестолкового игрока в информированного игрока в лото.
Проще говоря, неправильные комбинации приводят к пустой трате денег.
Правильный выбор комбинации приводит к хорошему броску в лотерее.
Благодаря комбинаторной математике и теории вероятностей, потому что у нас есть возможность узнать, действительно ли вы на правильном пути.
Например, комбинация, такая как 1-2-3-4-5-6, будет демонстрировать различную вероятность против 5-17-21-37-39-43 и 4-10-18-22-36-48.
Конечно, приведенные выше цифры – это только три из множества комбинаций в лотереях 6/49, которые имеют наименьший шанс получить ничью.
Давайте обсудим почему.
Почему комбинации не показывают равную вероятность?
Позвольте мне объяснить с использованием двух простых типов мрамора в банке. Желтый и красный цвет мрамора представляют типы комбинаций в лотерее.

Как видите, желтый мрамор превосходил пять красных. Вероятность объясняет, что когда вы случайно выберете мрамор из банки с закрытыми глазами, вы, скорее всего, получите желтый.
Ваш второй и третий выбор снова будут скорее желтыми, потому что вероятность того, что желтые шарики будут выбраны чаще, чем красные, будет выше.
В математике мы выражаем вероятность двух типов мрамора следующими способами:
P (желтый) = 95/100 или 95%
P (красный) = 5/100 или 05%
В десятичных представлениях мы выражаем измерение вероятности следующим образом:
P (желтый) = 95/100 или 0,95
P (красный) = 5/100 или 0,05
Предполагая, что мы сбрасываем количество шариков в каждом испытании, желтые шарики будут выбраны 95 раз за каждые 100 розыгрышей. Тогда красные шарики будут собираться только 5 раз в каждые 100 розыгрышей.
Ожидаемая частота (желтый шар) = 100 х 0,95 = 95 раз
Ожидаемая частота (красный шар) = 100 х 0,05 = 5 раз
Тот же принцип вероятности правил в случайной игре, такой как лотерея.
Позвольте мне привести некоторые убедительные доказательства того, что комбинации в лотерее действительно имеют разные вероятности.
Нечетные / четные комбинации
Давайте сгруппируем 49 чисел в два набора.
Нечетное = {1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19,21,23,25,27,29,31,33,35,37,39,41,43,45,47 , 49}
Четный = {2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20,22,24,26,28,30, 32,34,36,38,40,42,44,46,48 }
У нас есть 25 нечетных чисел и 24 четных числа.
Два набора представляют 49 шаров в игре Lotto 6/49.
Из этих 2 наборов мы можем изготовить следующие типы комбинаций:

Каждый нечетный / четный шаблон содержит определенное количество возможных комбинаций. Их общее количество представляет все возможные комбинации в игре «Лотерея 6/49», что составляет 13 983 816. И сумма всех их вероятностей должна быть равна 1.
Из таблицы выше мы видим, что это 3-четный-3-четный паттерн, который демонстрирует наилучшую вероятность быть втянутым в игру лотереи 6/49. Ожидается, что эта группа комбинаций произойдет 33 раза за 100 розыгрышей.
И, соответственно, те комбинации, которые состоят из всех четных или нечетных чисел, являются худшими комбинациями.
Примечательно, что некоторые комбинации не относятся ни к категории лучших, ни к худшим. Эти комбинации считаются средними. Использование этих групп комбинаций зависит от вашего решения.
Приведенные ниже таблицы должны показать всем игрокам лотереи 6/49, какие комбинации играть в лотерее 6/49.
Рекомендуемые комбинации

Комбинации среднего типа
(играть с этими комбинациями зависит от вас)

Комбинации, которых следует избегать

Фактические результаты лотереи в сравнении с теоретическим расчетом
Я показал, что комбинации не имеют равных шансов получить с теоретической точки зрения.
Теперь давайте докажем это, сравнив наш расчет с фактическими результатами лотереи.
Как я уже сказал, мы используем вероятность, чтобы измерить, насколько вероятна комбинация в данном количестве розыгрышей. Таким образом, умножив значение вероятности на определенное количество розыгрышей, мы получим ожидаемую частоту комбинации в данном заданном количестве розыгрышей.
Ожидаемая частота = вероятность х количество розыгрышей
И чтобы доказать, что наши теоретические расчеты верны, ожидаемая частота должна точно соответствовать фактической частоте.
Розыгрыш австралийского субботнего лото
664 с 7 января 2006 года по 29 сентября 2018 года

Можете ли вы заметить близкое соответствие между ожидаемой частотой и фактической частотой?
Обратите внимание, что вероятность – это просто руководство. Не ожидайте, что значения всегда будут совпадать. Иногда они делают.
Конечно, этот вероятностный анализ относится не только к австралийской лотерее. Теория вероятностей применима ко всем лотерейным системам.
И, как вы видите, приведенная выше таблица доказывает, что комбинаторные группы не имеют равной вероятности.
Давайте перейдем к другим системам лотереи, чтобы доказать нашу точку зрения дальше.
Американский Powerball
309 ничья с 7 октября 2015 года по 29 сентября 2018 года

Примечание: наш анализ Powerball США должен начаться 7 октября 2015 года, потому что это была дата, когда сотрудники лотереи начали внедрять формат 5/69.
Если вы заметили это, как теоретическая вероятность, так и фактические результаты лотереи сходятся в том, что комбинаторные группы имеют разные вероятности. И мы можем доказать это снова и снова.
Следующие таблицы ниже должны говорить сами за себя.
Миллионы евро
1 135 раздач с 16 апреля 2004 года по 28 сентября 2018 года

Евро Джекпот
340 разыгрывается с 23 марта 2012 года по 28 сентября 2018 года

Ирландское лото
320 разыгрывается с 5 сентября 2015 года по 29 сентября 2018 года

US Mega Millions
96 всего розыгрышей с 31 октября 2017 года по 28 сентября 2018 года

Примечание. Наш анализ Mega Millions в США должен начаться 31 октября 2017 года, потому что это была дата, когда сотрудники лотереи начали внедрять формат 5/70.
Лотерея Великобритании
309 тираж с 10 октября 2015 года по 29 сентября 2018 года

Низкие / Высокие комбинации
Помимо нечетных и четных, числа могут быть сгруппированы в низкие и высокие. Давайте сгруппируем 49 чисел в два набора:
Низкий = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24 , 25}
Высокий = {26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49 }
Из этих двух наборов наш анализ вероятности показывает, что выигрышные числа имеют тенденцию равномерно распределяться по всему полю чисел, так как большинство выигрышных комбинаций состоят из 3 чисел из нижнего набора и трех чисел из более высокого набора.
Точно так же игрокам рекомендуется держаться подальше от комбинации, которая состоит из чисто низких или чисто больших чисел.
Ниже приведены таблицы, показывающие все типы комбинаций, которые мы можем получить из двух наборов младших и старших чисел.
Рекомендуемые комбинации

Комбинации среднего типа
(играть с этими комбинациями зависит от вас)

Шаблоны, которых следует избегать

Фактические результаты лотереи в сравнении с теоретическим расчетом
Опять же, как теоретический расчет, так и фактические результаты лотереи сходятся в том, что некоторые комбинации работают лучше, чем другие.
Взгляните на следующие таблицы ниже:
Австралийское субботнее лото
664 разыгрывается с 7 января 2006 года по 29 сентября 2018 года

Американский Powerball
309 ничья с 7 октября 2015 года по 29 сентября 2018 года

Примечание: наш анализ Powerball США должен начаться 7 октября 2015 года, потому что это была дата, когда сотрудники лотереи начали внедрять формат 5/69.
Миллионы евро
1 135 раздач с 16 апреля 2004 года по 28 сентября 2018 года

Евро Джекпот
340 разыгрывается с 23 марта 2012 года по 28 сентября 2018 года

Ирландское лото
320 разыгрывается с 5 сентября 2015 года по 29 сентября 2018 года

US Mega Millions
96 тянет с 31 октября 2017 года по 28 сентября 2018 года

Примечание. Наш анализ «Мегамиллионов США» должен начаться 31 октября 2017 года, потому что это была дата, когда сотрудники лотереи начали внедрять формат 5/70.
Лотерея Великобритании
309 тираж с 10 октября 2015 года по 29 сентября 2018 года

Что дальше?
Анализ вероятностей может быть проблематичным и довольно запутанным.
Например, комбинация, такая как 1-2-3-4-5-6, состоит из 3-нечетных-3-четных чисел. Согласно нашему нечетному / четному анализу, такая комбинация считается одной из лучших.
Но мы знаем, что это неправда, потому что, наоборот, из нашего анализа низкого / высокого уровня, комбинация, состоящая из чисто малых чисел, обладает меньшей вероятностью.
Toutes les combinaisons de la loterie ont une probabilité égale d’être tirées car il n’y a qu’une seule façon de gagner le jackpot.

Cela signifie-t-il donc que 5-10-15-20-25-30 est tout aussi probable?
Non.
Vous voyez, si vous continuez à regarder la loterie d’un point de vue unilatéral, vous vous empêchez en quelque sorte de voir l’image entière.
Vous devez comprendre que la combinaison a une composition de nombres.
Et la composition compte.
À la loterie, les combinaisons sont regroupées en groupes combinatoires. Et les groupes combinatoires ont une probabilité différente.
Si vous choisissez de choisir votre combinaison dans un mauvais groupe, votre probabilité de gagner sera considérablement affectée.
Et vous continuez probablement à jouer des combinaisons avec une très faible probabilité.
Quelle est la preuve?
Eh bien, je suppose que la meilleure preuve est de vous montrer quelques calculs, puis d’utiliser les tirages de loterie réels pour prouver mon calcul.
Avec l’utilisation de la théorie des probabilités, nous pouvons calculer comment une combinaison se produira probablement dans un tirage. Nous pouvons mesurer la différence entre les meilleures combinaisons et les pires.
Malheureusement, le calcul des probabilités diffère d’une loterie à l’autre. Il n’y a pas de calcul unique.
Donc, à titre d’illustration, je vais utiliser le système de loto 6/49 comme base. Ne t’inquiète pas. Vous pourrez voir le calcul dans votre système de loterie préféré dans la section calculatrice.
Vous trouverez ci-dessous un exemple de combinaisons dans un système de loto 6/49.

Une combinaison composée de tous les nombres pairs ne peut se produire qu’une fois sur 100 tirages alors qu’une combinaison impaire et paire équilibrée peut se produire 33 fois sur 100 tirages.
Si nous voulons savoir comment ces deux groupes se produiront en 1000 tirages, il suffit de multiplier le nombre de tirages par leur probabilité correspondante.

Les chiffres ne mentent pas.
Ce pouvoir prédictif de probabilité vous aidera à devenir un joueur désemparé en un joueur de loto averti.
Autrement dit, de mauvaises combinaisons conduisent à un gaspillage d’argent.
Le bon choix de combinaison mène à un bon tir à la loterie.
Merci aux mathématiques combinatoires et à la théorie des probabilités car nous avons les moyens de savoir si vous êtes ou non sur la bonne voie.
Par exemple, une combinaison telle que 1-2-3-4-5-6 présentera une probabilité différente contre 5-17-21-37-39-43 et 4-10-18-22-36-48.
Bien sûr, les chiffres ci-dessus ne sont que trois des nombreuses combinaisons de jeux de loto 6/49 qui ont le plus de chances de se faire tirer.
Voyons pourquoi.
Pourquoi les combinaisons ne présentent-elles pas une probabilité égale?
Laissez-moi vous expliquer l’utilisation de deux types simples de billes dans un bocal. Les marbres de couleur jaune et rouge représentent les types de combinaisons de la loterie.

Comme vous le voyez, les billes jaunes étaient plus nombreuses que les cinq billes rouges. La probabilité explique que lorsque vous choisissez au hasard une bille dans un bocal les yeux fermés, vous en obtiendrez plus probablement une jaune.
Vos deuxième et troisième choix seront à nouveau des billes jaunes plus probables, car la probabilité se dirige vers les billes jaunes qui sont sélectionnées plus souvent que les rouges.
En mathématiques, nous exprimons la probabilité des deux types de billes de la manière suivante:
P (jaune) = 95/100 ou 95%
P (rouge) = 5/100 ou 05%
Dans les présentations décimales, nous exprimons la mesure de probabilité de la manière suivante:
P (jaune) = 95/100 ou 0,95
P (rouge) = 5/100 ou 0,05
En supposant que nous réinitialisons le nombre de billes dans chaque essai, les billes jaunes seront sélectionnées 95 fois tous les 100 tirages. Ensuite, les billes rouges ne seront cueillies que 5 fois tous les 100 tirages.
Fréquence attendue (boule jaune) = 100 x 0,95 = 95 fois
Fréquence attendue (boule rouge) = 100 x 0,05 = 5 fois
Le même principe de probabilité règne dans un jeu aléatoire comme la loterie.
Permettez-moi de vous donner des preuves solides que, en effet, les combinaisons de loterie présentent des probabilités différentes.
Combinaisons paires / impaires
Regroupons 49 numéros en deux ensembles.
Impair = {1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19,21,23,25,27,29,31,33,35,37,39,41,43,45,47 , 49}
Pair = {2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20,22,24,26,28,30, 32,34,36,38,40,42,44,46,48 }
Nous avons 25 nombres impairs et 24 nombres pairs.
Les deux sets représentent les 49 boules d’une partie de Lotto 6/49.
Sur ces 2 ensembles, nous pouvons produire les types de combinaisons suivants:

Chaque motif pair / impair contient un certain nombre de combinaisons possibles. Leur total représente toutes les combinaisons possibles dans un jeu de loto 6/49, soit 13 983 816. Et la somme de toutes leurs probabilités devrait être égale à 1.
Dans le tableau ci-dessus, nous voyons que c’est le modèle 3-impair-3-pairs qui présente la meilleure probabilité d’être tiré dans un jeu de loto 6/49. Ce groupe de combinaisons devrait se produire 33 fois en 100 matchs nuls.
Et en conséquence, les combinaisons qui consistent en tous les nombres pairs ou impairs sont les pires combinaisons.
De manière notable, certaines combinaisons ne sont ni classées comme les meilleures ni les pires. Ces combinaisons sont considérées comme les moyennes. L’utilisation de ces groupes de combinaisons dépend de votre jugement.
Les tableaux ci-dessous devraient guider tous les joueurs du loto 6/49 sur les combinaisons à jouer lors d’un tirage au sort 6/49.
Combinaisons recommandées

Combinaisons de type intermédiaire
(vous pouvez jouer avec ces combinaisons)

Combinaisons à éviter

Résultats réels de la loterie et calcul théorique
J’ai montré que les combinaisons n’ont pas autant de chances d’être attirées d’un point de vue théorique.
Maintenant, prouvons-le en comparant notre calcul avec les résultats réels de la loterie.
Comme je l’ai dit, nous utilisons la probabilité pour mesurer la probabilité qu’une combinaison se produise dans un nombre donné de tirages. Ainsi, en multipliant la valeur de probabilité par un certain nombre de tirages, nous obtenons la fréquence attendue de la combinaison dans ce nombre donné de tirages.
Fréquence attendue = Probabilité x nombre de tirages
Et pour prouver que notre calcul théorique est correct, la fréquence attendue doit correspondre étroitement à la fréquence réelle.
Australian Saturday Lotto
664 tirages du 7 janvier 2006 au 29 septembre 2018

Pouvez-vous remarquer la correspondance étroite entre la fréquence attendue et la fréquence réelle?
Prenez note que la probabilité est simplement un guide. Ne vous attendez pas à ce que les valeurs correspondent toujours. Parfois, ils le font.
Bien entendu, cette analyse de probabilité ne s’applique pas uniquement à la loterie australienne. La théorie des probabilités s’applique à tous les systèmes de loterie.
Et comme vous le voyez, le tableau ci-dessus prouve que les groupes combinatoires n’ont pas la même probabilité.
Passons à d’autres systèmes de loterie pour prouver notre point plus loin.
US Powerball
309 tire du 7 octobre 2015 au 29 septembre 2018

Remarque: Notre analyse du Powerball américain doit commencer le 7 octobre 2015, car c’est la date à laquelle les responsables de la loterie ont commencé à mettre en œuvre le format 5/69.
Si vous le remarquez, les probabilités théoriques et les résultats réels de la loterie conviennent que les groupes combinatoires ont des probabilités différentes. Et nous pouvons le prouver encore et encore.
Les tableaux ci-dessous devraient parler d’eux-mêmes.
Euro Millions
1135 tirages du 16 avril 2004 au 28 septembre 2018

L’Euro Jackpot
340 se déroule du 23 mars 2012 au 28 septembre 2018

Irish Lotto
320 tire du 5 septembre 2015 au 29 septembre 2018

US Mega Millions
96 tirages au total Du 31 octobre 2017 au 28 septembre 2018

Remarque: Notre analyse des Mega Millions américains doit commencer le 31 octobre 2017, car c’est la date à laquelle les responsables de la loterie ont commencé à mettre en œuvre le format 5/70.
UK Lottery
309 tire du 10 octobre 2015 au 29 septembre 2018

Combinaisons basses / hautes
Mis à part les nombres pairs et impairs, les nombres peuvent être groupés en bas et en haut. Regroupons 49 numéros en deux ensembles:
Faible = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24 , 25}
Élevé = {26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49 }
Sur ces deux ensembles, notre analyse des probabilités montre que les numéros gagnants ont tendance à être répartis uniformément dans l’ensemble du champ numérique, car la majorité des combinaisons gagnantes se composent de 3 numéros de l’ensemble inférieur et de trois nombres de l’ensemble supérieur.
De même, les joueurs sont encouragés à rester loin d’une combinaison qui consiste en des nombres purement bas ou des nombres purement élevés.
Voici les tableaux montrant tous les types de combinaisons que nous pouvons produire à partir des deux ensembles de nombres bas et hauts.
Combinaisons recommandées

Combinaisons de type intermédiaire
(vous pouvez jouer avec ces combinaisons)

Modèles à éviter

Résultats réels de la loterie et calcul théorique
Encore une fois, le calcul théorique et les résultats réels de la loterie conviennent que certaines combinaisons fonctionnent mieux que d’autres.
Jetez un œil aux tableaux suivants:
Australian Saturday Lotto
664 tirages du 7 janvier 2006 au 29 septembre 2018

US Powerball
309 tire du 7 octobre 2015 au 29 septembre 2018

Remarque: Notre analyse du Powerball américain doit commencer le 7 octobre 2015, car c’est la date à laquelle les responsables de la loterie ont commencé à mettre en œuvre le format 5/69.
Euro Millions
1135 tirages du 16 avril 2004 au 28 septembre 2018

L’Euro Jackpot
340 se déroule du 23 mars 2012 au 28 septembre 2018

Irish Lotto
320 tire du 5 septembre 2015 au 29 septembre 2018

US Mega Millions
96 tirages du 31 octobre 2017 au 28 septembre 2018

Remarque: Notre analyse des US Mega Millions doit commencer le 31 octobre 2017, car c’est la date à laquelle les responsables de la loterie ont commencé à mettre en œuvre le format 5/70.
UK Lottery
309 tire du 10 octobre 2015 au 29 septembre 2018

Et après?
L’analyse de probabilité peut être problématique et assez déroutante.
Par exemple, une combinaison telle que 1-2-3-4-5-6 consiste en 3 nombres pairs-3 impairs. Selon notre analyse paire / impaire, une telle combinaison est considérée comme l’une des meilleures.
Mais nous savons que ce n’est pas vrai parce qu’à l’inverse de notre analyse basse / haute, une combinaison qui est faite de petits nombres possède une probabilité inférieure.